Health and safety offences, corporate manslaughter and food safety and hygiene offences definitive guideline
On 3 November 2015 the Sentencing Council published Health and Safety Offences, Corporate Manslaughter and Food Safety and Hygiene Offences Definitive Guideline. This provides new guidance for sentencing in relation to health and safety, corporate manslaughter and food safety and hygiene. It was issued following a consultation to ensure a consistent, fair and proportionate approach to sentencing and came into effect on 1 February 2016.
Offences covered by the guidance could, for example, include contractors that cause the death of an employee by not providing proper equipment, a manufacturer that causes injury to a new worker by not providing proper training, or a gas fitter whose work leads to the risk of an explosion.
The guidance sets out sentencing ranges that reflect different levels of risk of harm that can result from offences. While prison sentences are available for individuals convicted of very serious offences, most are committed by organisations that can only be fined. In most cases the new guidance will not result in significantly higher fines, however, some offenders will receive higher penalties, for example, an organisation deliberately breaking the law and creating a high risk of death or serious injury.
This is intended to ensure fines properly reflect the crimes committed. The sentencing ranges also take into account how culpable the offender was. This could range from minor failings in procedures to deliberately dangerous acts.
The guidance uses the turnover of the offender as the starting point for determining the fine, but must take into account other relevant financial information, such as profit margin, the potential impact on employees, the potential impact on the organisation’s ability to improve conditions or to make restitution to victims and so on. It also includes mitigating factors which allow for voluntary positive action to remedy a failure on the part of offenders to be reflected in sentences. Remedial orders can be made by the court where appropriate.
Sentencing Council member Michael Caplan QC said, “These guidelines will introduce a consistent approach to sentencing, ensuring fair and proportionate sentences for those who cause death or injury to their employees and the public or put them at risk. These offences can have very serious consequences and it is important that sentences reflect these.”
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki.
Featured articles and news
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
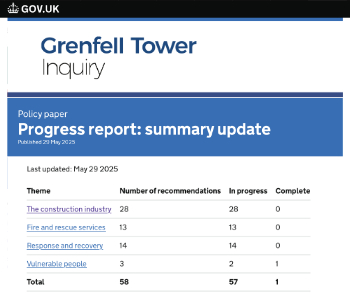
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.